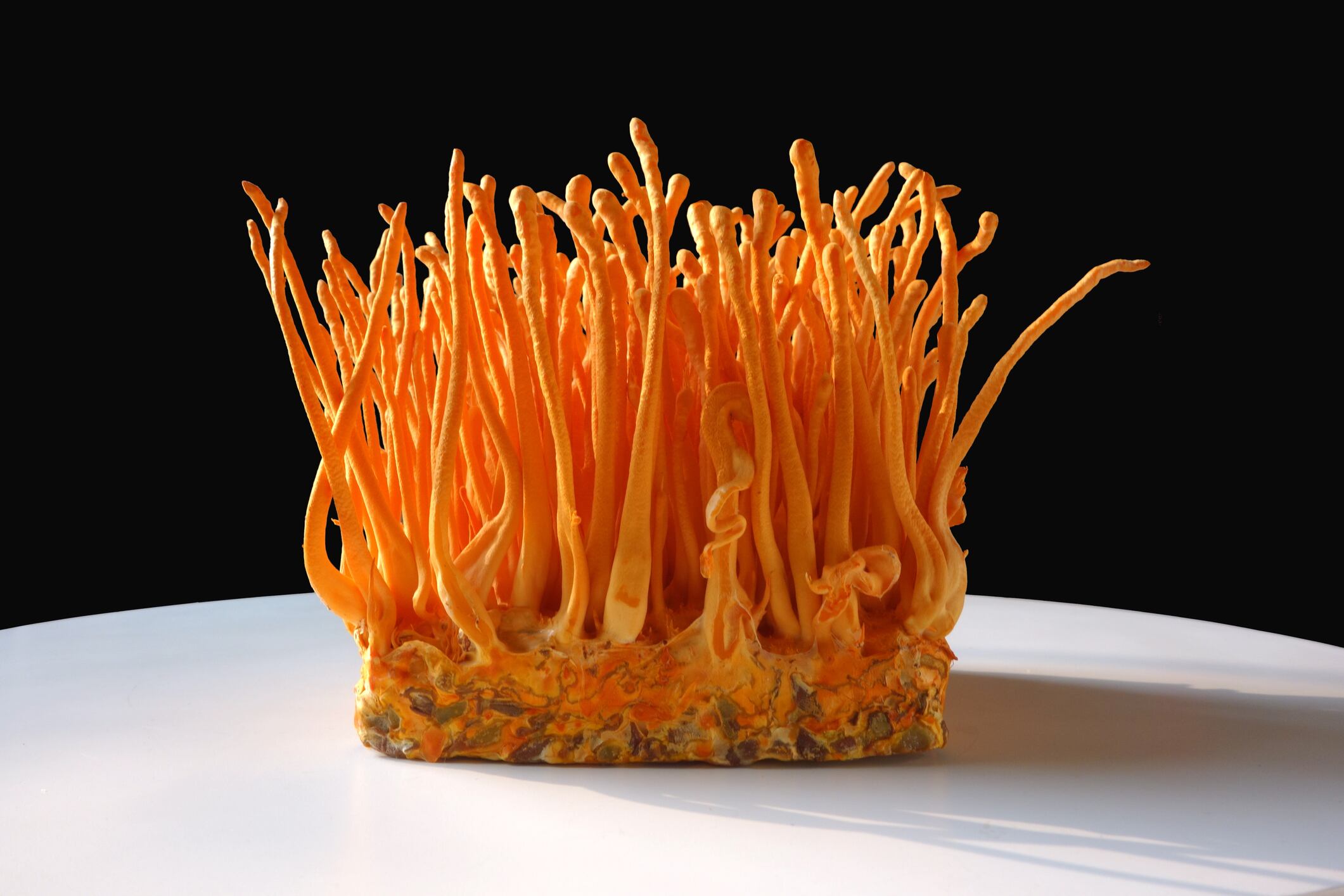
The standing is just like Cordyceps sinensis, often known as ‘caterpillar fungus’, which was confirmed as not novel earlier this yr. Nevertheless, the mycelium and fruiting physique of one other species, often called Cordyceps militaris, stays novel in accordance with the Novel Meals catalogue.
Whereas the ruling is optimistic and ‘lengthy overdue’, it may trigger confusion within the business, in accordance with Robin Gurney, director of the Estonia-based mushroom extract provider Musheez.
It is because S. hepiali is often recognized and bought as cordyceps however truly belongs to a distinct genus.
Cordyceps vs S. hepiali
Predominantly discovered within the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau area of China, cordyceps historically refers to Ophiocordyceps sinensis. Generally known as the ‘winter worm’ or ‘summer season grass’, this fungus species may be very uncommon and should even be thought of endangered.
The species has been used for tons of of years in Chinese language medication, with analysis displaying the fungus could help stamina, vitality and lung and kidney well being.
Nevertheless, on condition that wild O. sinensis is in scarce provide, it has turn out to be an especially costly commodity, typically costing 1000’s of euros per kilogram, in accordance with Gurney.
For that reason, S. hepiali has successfully turn out to be a alternative for O. sinensis in dietary dietary supplements throughout the globe.
“S. hepiali belongs to the identical fungal household— Cordycipitaceae—however is a distinct genus from O. sinensis,” Gurney mentioned.
“The well-known Cs-4 pressure was initially considered O. sinensis, however genetic research confirmed it’s in actual fact S. hepiali. For this reason many merchandise within the West labelled ‘Cordyceps sinensis Cs-4’ are technically S. hepiali Cs-4.”
The benefit of S. hepiali is that it may be cultivated at scale by liquid fermentation, offering a secure, dependable and sustainable provide, he added.
It additionally delivers the identical key compounds as wild cordyceps —resembling cordycepin, adenosine, polysaccharides, mannitol and sterols—which underpin its anti-fatigue, immune-supportive and metabolic advantages.
“The great thing about S. hepiali is that it delivers the identical key compounds as wild cordyceps, however it may be produced safely and sustainably,” Guerney mentioned.
May labeling necessities change?
So, is S. hepiali simply as secure and efficient as wild cordyceps? Gurney appears to assume so, noting that confusion merely stems from labeling inaccuracies.
“[S. hepiali] is a well-studied ingredient, used safely in tons of of merchandise the world over and even bought as prescription medication in China,” he mentioned. “For many years, Cs-4 has largely been bought as ‘Cordyceps sinensis Cs-4.’ Scientifically that’s inaccurate, however commercially it has caught.”
Gurney believes the latest replace on S. hepiali’s standing as a non-novel meals is unlikely to trigger any modifications to labeling necessities. Nevertheless, it might trigger extra correct labeling to emerge.
“At Musheez, we’re contemplating amending bulk labeling and product sheets within the gentle of this ruling,” he mentioned. “We are going to go away our personal label shoppers to resolve what is suitable for his or her case.”
By way of influence, Gurney says the choice will create regulatory certainty for the EU complement business, which is more likely to influence the provision and recognition of cordyceps-type dietary supplements.
“The EU ruling places S. hepiali on the identical footing as O. sinensis—each can now be utilized in meals dietary supplements, giving manufacturers certainty and shoppers extra alternative,” he mentioned. “The choice will in all probability imply greater and wider availability of ‘cordyceps-type’ dietary supplements. As soon as this data is absolutely digested, I anticipate we are going to see a cordyceps increase.”