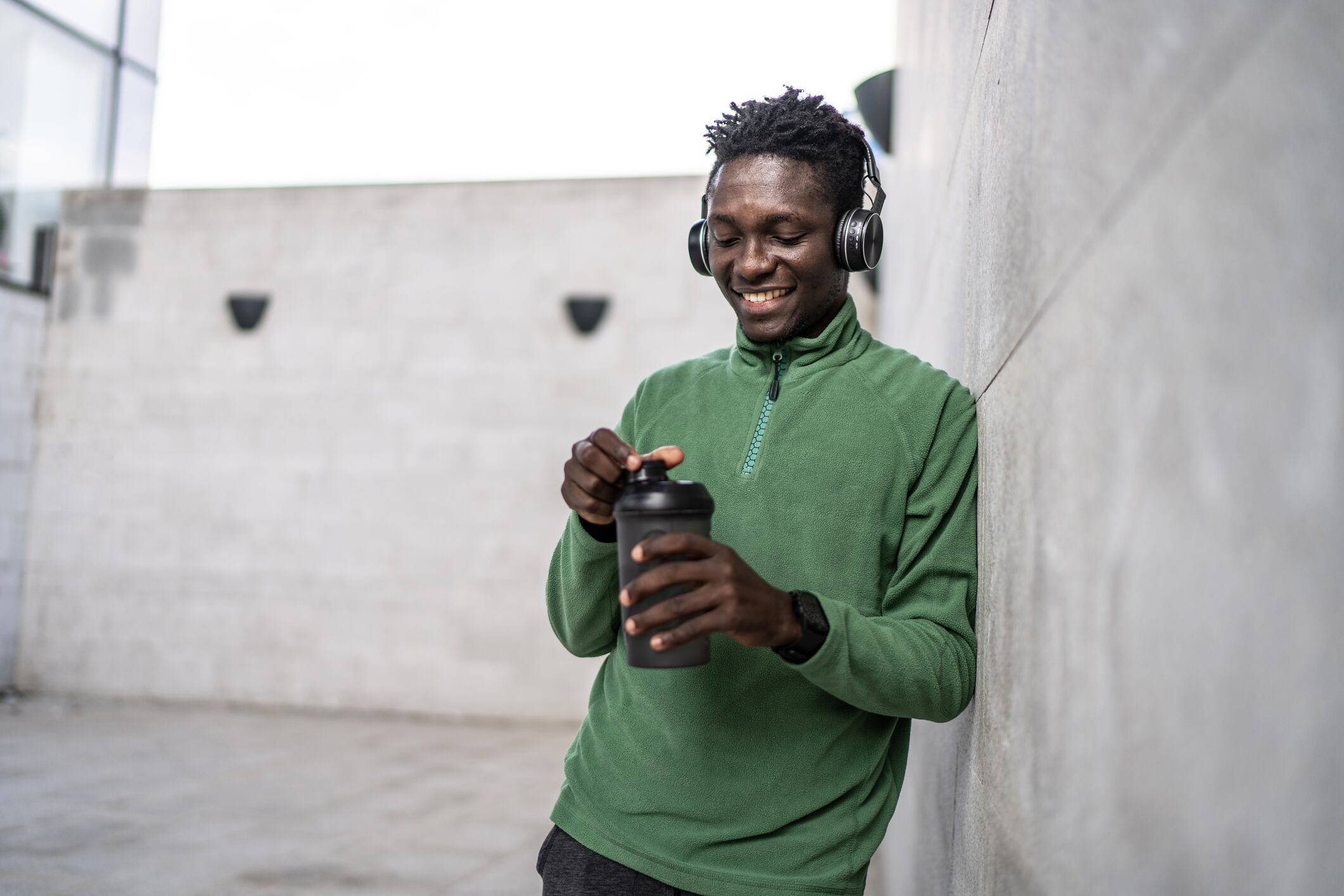
Regardless of being poor in lots of important nutritional vitamins and vitamins, protein has garnered shoppers’ consideration. However why?
Low carb, low sugar, low fats however excessive in protein. It’s the magical buzzword that continues to sway buying energy.
Nonetheless, the common particular person wants not more than round 55g of protein per day, based on the British Coronary heart Basis. However many merchandise in the marketplace declare to supply over half that RDA.
Even for somebody trying to construct muscle supported by fitness center exercise, the advisable protein consumption doesn’t creep up a lot increased than 60g per day.
How massive is the meals protein market?
But the marketplace for useful meals containing protein is predicted to rocket by over €44bn in the next three years.
BBC Science just lately claimed food and drinks firms had quadrupled the variety of high-protein merchandise on the cabinets as a result of they’re income drivers, not as a result of shoppers are protein poor.
What’s behind it? Predominantly social media and social influencers, with mentions of protein rising by over 10% year-on-year for some platforms.
Inside this, the demonisation of fat and carbohydrates has additionally pushed up shoppers’ want for elevated protein ranges as they think about it an important ingredient for a nutritious diet.
Excessive-protein diets that work
Excessive-protein diets of the previous and current, together with Paleo, Atkins, Zone and Dunkan, have advocated individuals eat increased ranges of fish, meat, eggs, nuts and cheese to drop extra pounds. Protein can improve satiety, which is how such diets typically work.
Basic dietary recommendation is 20% of a weight-reduction plan needs to be protein to keep up weight and as much as 25% to drop extra pounds.
Regardless of the positives for gross sales, weight reduction and different components, some scientists argue high protein diets can lead to serious health issues, resembling heart problems, particularly from animal-derived proteins.
Plant-proteins have been thought of more healthy, particularly as they contained increased ranges of fibre, phytochemicals and unsaturated fat.