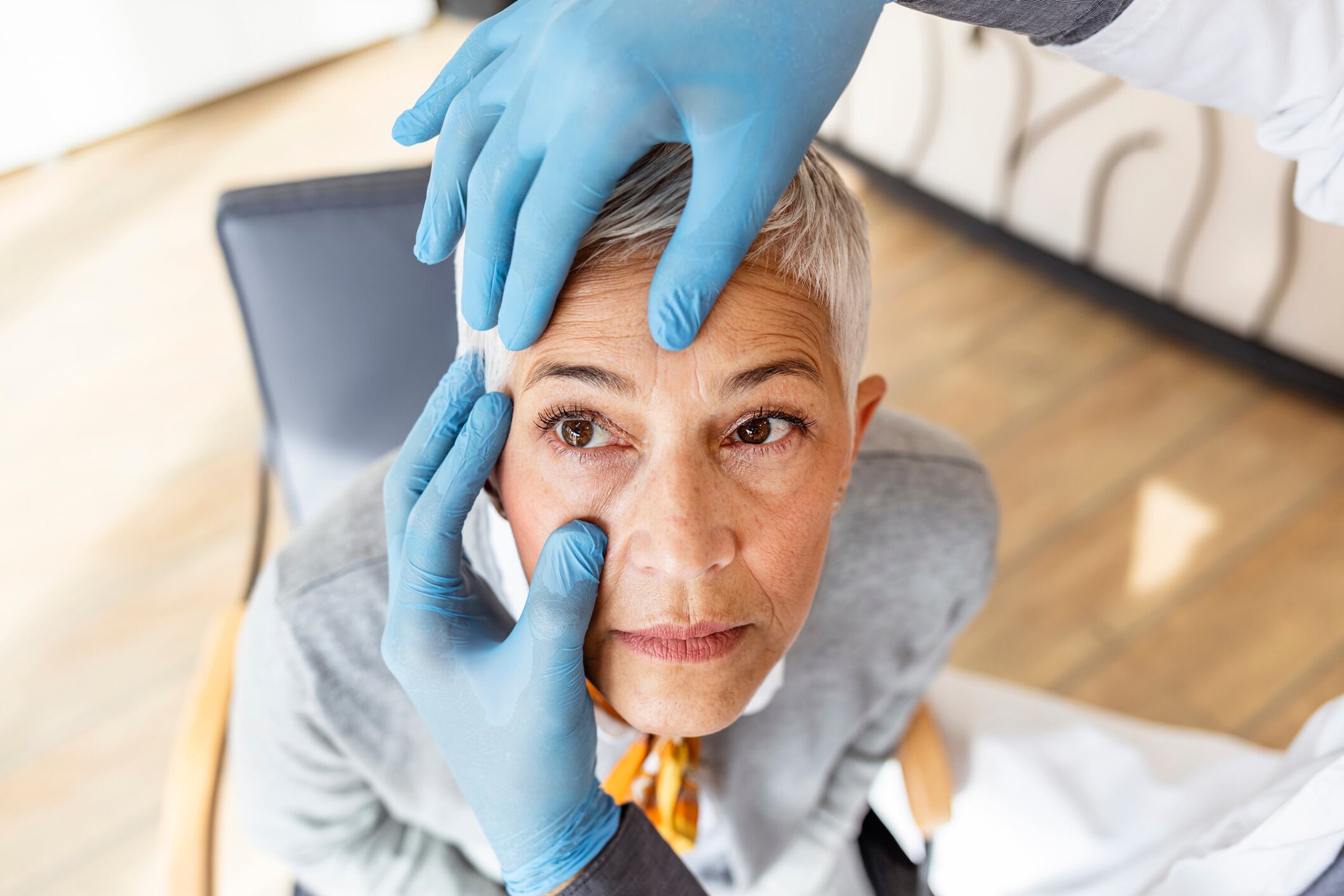
Researchers in Taiwan carried out a randomized managed trial on 52 ophthalmology sufferers. Their outcomes indicated the complement’s helpful results and revealed potential mechanisms implicated in dry-eye syndrome (DES).
“These findings assist the potential of focused dietary supplementation as a protected and efficient technique for assuaging DES signs, providing a substitute for typical therapies that completely deal with symptom administration,” they wrote in Antioxidants.
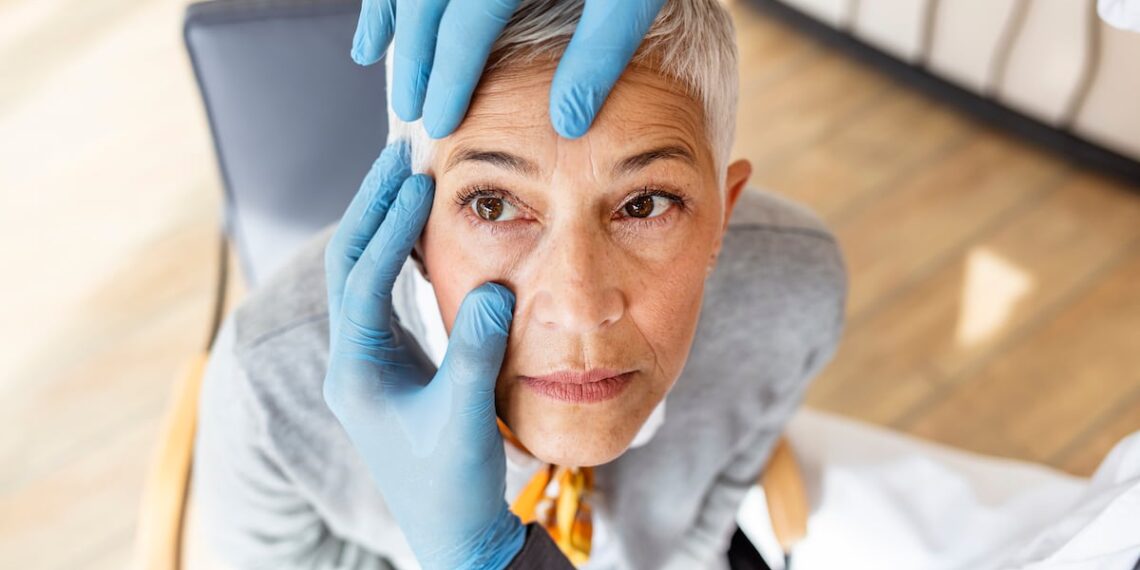
Dry eye syndrome
Dry eye syndrome impacts between 10% and 30% of Europeans, inflicting signs of discomfort and visible impairment. Experts clarify that DES occurs when the eyes don’t make sufficient tears to remain moist or when the tears don’t work appropriately.
Individuals over the age of fifty, girls with hormonal adjustments equivalent to being pregnant or menopause, those that take a look at screens for lengthy durations and speak to lens wearers could also be extra in danger.
The present research famous that irritation is a key mechanism underlying DES. Individuals with the situation could develop an adaptive immune response leading to “decreased lacrimal secretion and related ocular floor discomfort.”
Useful vitamins
Recent research highlights the affect of food regimen, suggesting that sure vitamins equivalent to omega-3 fatty acids, protein and nutritional vitamins A, C and E are related to a decrease threat of DES.
These vitamins assist to deal with the irritation and oxidative stress related to the situation.
Lutein and zeaxanthin are acknowledged to be helpful for eye well being, serving to to soak up blue mild and defending the retina from injury. Their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties could assist to control the immune response, and former research counsel they enhance tear manufacturing.
Research particulars
Researchers randomly assigned 52 individuals between the ages of 20 and 80 with average or extreme DES to take a complement containing 45 mg/day EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid), 30 mg/day DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), 30 mg/day lutein and 1.8 mg/day zeaxanthin or placebo for 12 weeks. Members maintained their traditional food regimen all through the research.
Assessments included Schirmer’s check and the ocular floor illness index (OSDI), blood or tear oxidative stress, antioxidant capacities and tear inflammatory indicators.
The outcomes confirmed a major enhance in tear secretion and a discount in OSDI scores in individuals taking the complement. Inflammatory markers, equivalent to interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-8, have been additionally decreased on this group.
“After 12-week supplementation, the complement group displayed a major OSDI lower of 6.6 factors in contrast with the management group, corroborating the antioxidant and anti inflammatory properties of fish oil, lutein and zeaxanthin,” the researchers wrote.
Additionally they famous that antioxidant capability and oxidative stress have been each lowered within the management group.
“This paradoxical commentary could replicate the complicated function oxidative stress performs within the medical development of DES,” they wrote. “The rise in oxidative stress might result in the depletion of antioxidant defenses, because the physique makes an attempt to counteract the damaging results of oxidative stress.
“Such depletion could characterize an adaptive response to continual oxidative stress, the place mobile protecting mechanisms have interaction antioxidants to neutralize dangerous free radicals.”
Supply: Antioxidants 2025, 14(1), 103. doi: 10.3390/antiox14010103. “Multicomponent Dietary Supplementation: Influence on Tear Secretion and Ocular Floor Irritation in Dry Eye Syndrome Sufferers”. Authors: S-C. Huang et al.