A current meta-analysis of 12 randomised managed trials (RCTs) involving 1,183 post-menopausal ladies revealed that probiotic supplementation considerably improved bone well being.
The examine, carried out by researchers on the Peking Union Medical Faculty Hospital, discovered that probiotics elevated bone mineral density (BMD) in each the lumbar backbone and hip whereas lowering markers of bone breakdown, equivalent to collagen sort 1 cross-linked C-telopeptide (CTX).
These advantages have been particularly pronounced in ladies with delicate bone loss — generally known as osteopenia — in comparison with these with extreme bone loss or osteoporosis. The findings prompt that probiotics might be a promising low-risk intervention for bone well being in postmenopausal ladies.
Why bone well being declines after menopause
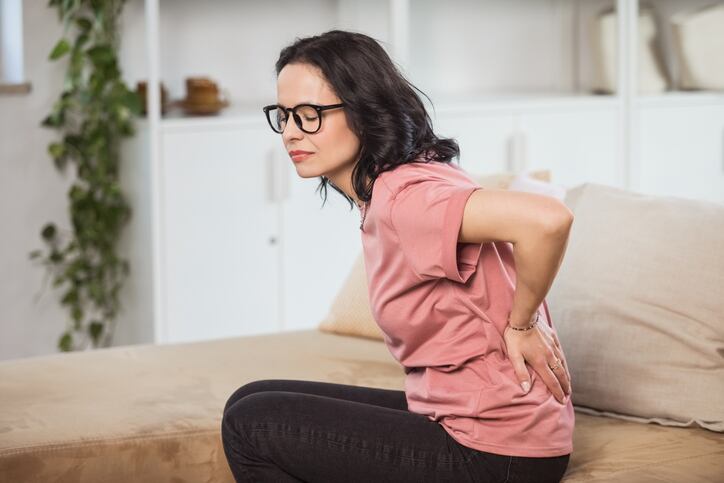
Postmenopausal ladies face a excessive threat of osteoporosis, a situation characterised by weakened bones and a better probability of fractures. This elevated vulnerability is basically on account of a decline in oestrogen ranges, which play a important position in sustaining bone power.
Through the early post-menopausal years, ladies can lose as much as 5% of their bone density yearly, leaving them extra prone to fractures, significantly within the backbone and hips. Though pharmaceutical therapies can be found, their long-term use is commonly restricted by unwanted side effects and poor adherence, driving curiosity in different methods equivalent to probiotics.
How probiotics affect bone well being
Probiotics are stay microorganisms that provide well being advantages when consumed in ample portions. Whereas they’re mostly related to intestine well being, analysis has proven that they’ll additionally affect bone metabolism via a number of mechanisms.
These embrace lowering irritation that accelerates bone loss, enhancing the absorption of vitamins needed for bone formation, and selling the manufacturing of short-chain fatty acids that assist steadiness bone formation and breakdown.
Animal research have demonstrated that probiotics can enhance bone density in fashions of osteoporosis however human analysis, particularly analysis targeted on post-menopausal ladies, has been inconsistent.
Probiotics’ impression on BMD and bone turnover markers
The meta-analysis examined the impression of probiotics on BMD and bone turnover markers (BTMs), which mirror the processes of bone formation and resorption.
The outcomes confirmed that ladies who took probiotics had considerably greater BMD within the lumbar backbone and hip in comparison with these within the management group.
This enchancment was extra pronounced in ladies with osteopenia, suggesting that probiotics is perhaps significantly efficient within the early phases of bone loss.
The evaluation additionally discovered that probiotics diminished CTX, a marker of bone resorption, and bone-specific alkaline phosphatase (BALP), which is linked to general bone turnover. Nonetheless, different markers equivalent to osteocalcin (OC) and receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL) didn’t present vital adjustments, indicating that probiotics primarily affect bone resorption reasonably than formation.
Components influencing probiotics’ effectiveness
The length and dosage of probiotic supplementation appeared to play a important position in figuring out its effectiveness.
Extended supplementation of over 12 months yielded higher enhancements in BMD than shorter therapy durations.
Moreover, greater doses (not less than one billion colony-forming items or CFUs per day) have been more practical than decrease doses.
The researchers additionally noticed regional variations, with European ladies displaying extra vital enhancements in BMD in comparison with Asian ladies.
This variation might be attributed to variations in intestine microbiota composition, dietary habits, or genetics, though additional analysis is required to totally perceive these disparities.
Implications for companies and healthcare suppliers
These findings have sensible implications for companies and healthcare suppliers. Probiotic producers have a chance to develop focused merchandise for bone well being, significantly these with greater dosages and designed for long-term use.
Healthcare suppliers, in the meantime, can take into account probiotics as a part of a broader technique for managing bone well being in post-menopausal ladies, particularly for these hesitant to make use of conventional medicines.
The examine additionally highlighted the necessity for additional analysis to establish particular probiotic strains and combos which might be simplest for bettering bone well being.
Limitations and conclusions
Regardless of its promising outcomes, the examine had a number of limitations. The included trials exhibited vital variability in methodology, and plenty of concerned co-interventions, equivalent to probiotics mixed with vitamin D or calcium. This made it tough to isolate the results of probiotics alone.
Moreover, the particular strains of probiotics answerable for the noticed advantages remained unclear.
Future analysis ought to deal with longer-term research, strain-specific results, and the position of intestine microbiota in particular person responses to probiotics.
The researchers concluded: “Probiotic supplementation might serve in its place method to decelerate bone mass deterioration in post-menopausal ladies with osteopenia. As well as, administration of probiotics may lower ranges of CTX and BALP. Sooner or later, extra analysis is required to validate these findings, and particular strains helpful for bone well being in postmenopausal ladies have to be additional explored.”
Supply: Frontiers in Endocrinology
“Results of probiotic supplementation on bone well being in postmenopausal ladies: a scientific assessment and meta-analysis”
https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2024.1487998
Authors: Fang Wang, et al.