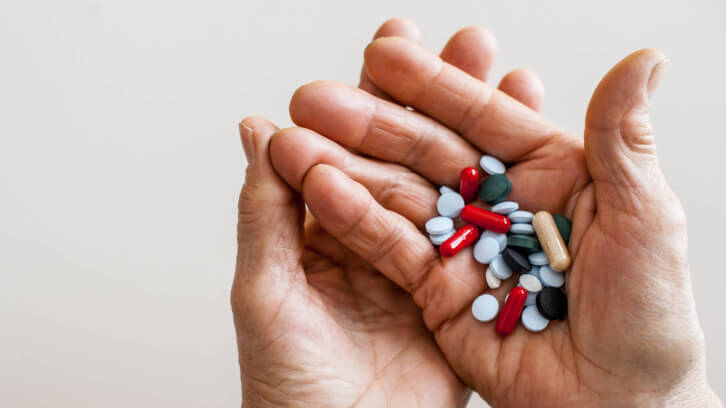
In a brand new paper revealed within the Journal of Dietary Dietary supplements, Invoice Gurley, PhD, principal scientist on the Nationwide Heart for Pure Merchandise Analysis on the College of Mississippi, appears again at three a long time of dietary complement utilization in a market that has developed from a couple of hundred merchandise made up principally of nutritional vitamins, minerals and choose botanical extracts to greater than 75,000 single- and multi-ingredient merchandise. Throughout this era, one of many fastest-growing segments has been merchandise formulated with botanicals.
“Coincident with the rising reputation of botanical dietary dietary supplements (BDS) has been their concomitant ingestion with standard prescription medicines,” Dr. Gurley famous. “BDS are advanced mixtures of phytochemicals oftentimes exhibiting advanced pharmacology.”
Formulated as concentrated phytochemical extracts, they include quite a lot of plant secondary metabolites hardly ever encountered within the typical food plan, he added, which when taken with prescribed drugs may result in clinically vital herb–drug interactions (HDI).
An extended historical past of plant drugs
Folks and animals have benefited from the therapeutic properties of crops for the reason that beginnings of time, with using botanical extracts establishing itself as phytomedicine throughout cultures over millennia.
Within the New World, botanicals have been a mainstay in American drugs from the earliest settlements when the primary colonists of the 17th century used quite a lot of imported and endemic herbs and traditions to deal with situations starting from dysentery to syphilis. Among the many hottest crops, roots and different pure merchandise have been snakeroot, dittany, senna, alum, candy gums and tobacco, based on historian Thomas P. Hugues, writing of the history of the medicine in the Jamestown settlement from 1607 to 1699.
America Pharmacopeia (USP), a compendium of requirements and high quality assessments for crops and herbs offered in chemist or druggist retailers, first revealed in 1820, and america Dispensatory (USD) served as a complimentary physique of high quality assessments and specs for confirming composition, purity, energy and makes use of from 1833 to 1973.
“For greater than 140 years, American physicians and pharmacists relied upon scholarly monographs revealed inside these two official compendia which detailed a litany of pharmaceutical preparations for treating varied ailments and illness signs; the overwhelming majority of those have been plant based mostly,” Dr. Gurley wrote. “Thus, botanical extracts with their multiplicity of plant secondary metabolites (PSM)—resident phytochemicals utilized in protection in opposition to herbivores, pathogens and different plant species—have been a driving power in American drugs all through the nineteenth century and the primary half of the twentieth century.”
The invention of antimicrobial sulfonamide medication, penicillin and different artificial and semi-synthetic antibiotics by the tip of World Conflict II, nonetheless, shifted the main focus away from plant-based medicines in the direction of single-ingredient artificial compounds and relegated pharmacognosy (the examine of medication derived primarily from crops) to the vestiges of pharmacy school curricula previous.
Citing Brinckmann et al. published in HerbalGram, Dr. Gurley famous that “by 1960, many botanicals and their officinal preparations that had loved prolonged tenures in each the USP and USD have been lastly ‘dismissed’ as a consequence of an absence of utilization amongst pharmacists and physicians.”
Resurrected from ‘the dustbin of medical historical past’
With the passage of DSHEA, herbs and different botanicals grew to become wrapped up and encoded within the definition of dietary dietary supplements together with nutritional vitamins, minerals, amino acids and dietary substances meant to complement the food plan (or any concentrates, metabolites, constituents, extracts or combos of the above).
A bunch referred to as the European-American Phytomedicines Coalition (EAPC) had been pushing for the creation of a separate OTC class for botanical medication within the lead as much as 1994, however this was met by resistance from a U.S. Meals and Drug Administration that didn’t see a spot for pure merchandise within the fashionable drug evaluate system on the time, Loren Israelsen, founder and president of the United Pure Merchandise Alliance and co-founder of the EAPC, previously told NutraIngredients-USA.
“The implementation of DSHEA resurrected botanical extracts from the dustbin of medical historical past, reworking them from conventional tinctures and elixirs into modern dosage varieties like capsules and tablets,” Dr. Gurley wrote. “One regarding facet of DSHEA, which hinted on the emergence of varied future well being points aligned with this revival, was its leniency towards regulatory oversight of botanical dietary dietary supplements (BDS).”
As botanical formulations started to flood the market, they have been now regulated like their complement contemporaries, having fun with entry with out the pre-market approval required of standard drug merchandise regardless of their phytomedicine previous and phytochemical elements.
“The mass inflow of BDS onto each U.S. and international markets introduced with it apprehensions concerning attainable BDS-mediated drug interactions,” Dr. Gurley famous, including that considerations have been realized in 2000 when St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum), used as an antidepressant, interacted with immunosuppressant drug cyclosporine, inflicting acute rejection in coronary heart transplant sufferers.
He instructed substantial potential for herb-drug interactions, referring to surveys displaying that 20% to 30% of prescription drug customers co-ingest medicines and natural dietary supplements and that 70% of BDS customers additionally take prescription medicines. Furthermore, older adults (40% to 70% of whom report common use of natural merchandise) face elevated odds of polypharmacy and age-related modifications in drug disposition.
“Polypharmacy coupled with BDS utilization, together with a hesitancy towards acknowledging such practices, place senior residents at elevated threat for HDI,” Dr. Gurley added.
Clinically related interactions
Herb-drug interactions presently fall into one among two classes: pharmacodynamic (interactions between phytochemicals and traditional medicines on the drug receptor degree) and the extra prevalent pharmacokinetic (stemming from BDS-mediated alterations in human drug metabolism and/or transport.)
Within the case of St. John’s wort, one of many extra studied botanicals on the planet, the pharmacokinetic interactions are tied to its hyperforin compound, which Dr. Gurley recognized as “a double-edged phytochemical sword” that inhibits broad-based neurotransmitter reuptake as an anti-depressant however enhances systemic clearance for greater than 70% of all prescription medicines.
Different botanicals on the paper’s clinically related pharmacokinectic HDI record: goldenseal (Hydrastis canadensis), black pepper (Piper nigrum), Schisandra spp., Berberis spp., Coptis spp. and extra not too long ago cannabidiol. Inexperienced tea (Camellia sinensis), resveratrol and quercetin are flagged as posing low to intermediate dangers primarily as a result of restricted variety of research designed to validate medical relevance fairly than therapeutic penalties of herb-drug interplay.
Concerning pharmacodynamic interactions, the evaluate summarized a historical past of results investigated in ephedra, ephedra-free dietary supplements (proprietary blends) and licorice root (Glycyrrhiza glabra).
The present data hole
“From the few summaries outlined above, the paucity of clinically related HDI candidates recognized over the previous 30 years is kind of shocking, given the burgeoning BDS market,” Dr. Gurley wrote. “It seems, nonetheless, that extremely common, extra acquainted BDS like black cohosh, curcumin, echinacea, garlic, ginseng, kava kava, milk thistle, noticed palmetto, valerian and lots of others harbor phytoconstituents which may be both inactive pharmacodynamically or ineffective pharmacokinetically.”
He additionally proposed components at play starting from phytochemical properties that hinder dissolution to lapses in adherence to present good manufacturing practices (e.g., correct characterization and verification, prevention of adulteration and contamination, assurance of dosage kind efficiency, correct product label claims).
The evaluate referred to as consideration to the unknowns and under-researched such because the influence of novel supply methods designed to spice up phytochemical absorption on HDI threat standing and the “lamentably missing” scientific consciousness of most pharmacists and physicians concerning BDS and HDI regardless of stories and books devoted to the subject. There may be additionally the consideration whether or not HDI studied in vivo translate to people.
“Happily, for physicians and pharmacists, the present threat for clinically related HDI appears pretty low; nonetheless, the overwhelming majority of BDS have but to be correctly evaluated, and in all probability they by no means will,” Dr. Gurley concluded. “Nonetheless, with regards to the co-ingestion of prescription medicines and BDS, shoppers and healthcare suppliers alike ought to all the time err on the facet of warning.”
Supply: Journal of Dietary Dietary supplements
doi: 10.1080/19390211.2024.2327544
“Clinically Related Herb–Drug Interactions: A 30-12 months Historic Evaluation”
Writer: Invoice J. Gurley