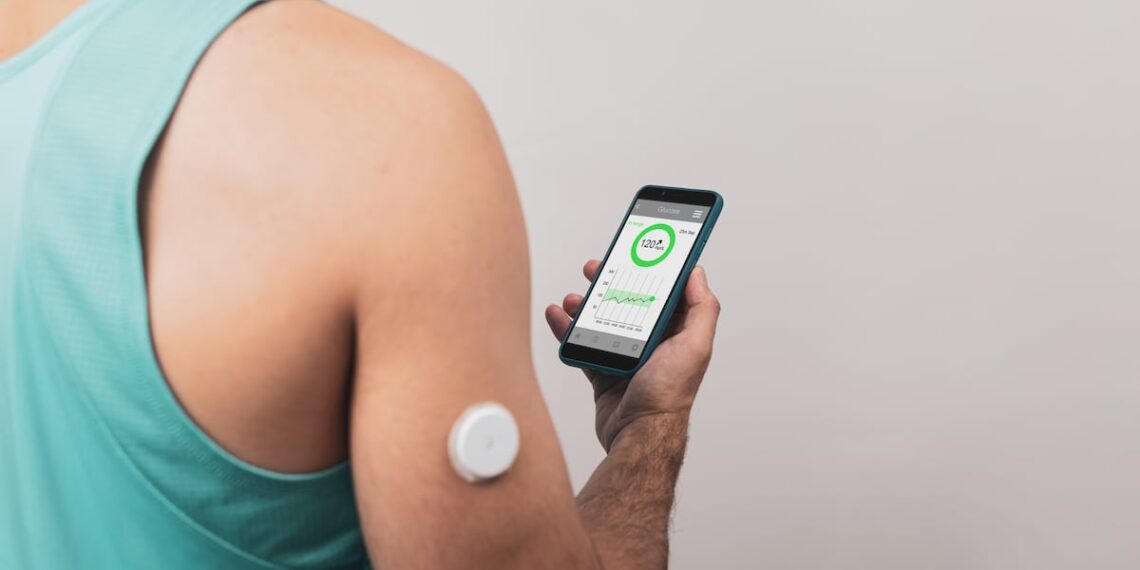
Printed within the journal Diabetes Remedy, findings confirmed that people taking the complement have a considerably decrease improve in post-meal blood glucose ranges, in addition to a considerably decrease glycemic variability as in comparison with the management group.
Research particulars
The randomized, managed, open-label, crossover examine recruited a complete of 42 people with sort 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and assigned them to a check or management group for 5 days. Following a three-day washout interval, the 2 teams swapped their breakfasts for the following 5 days.
The check product used was Protinex Diabetes Care, a low-GI, high-protein, fiber-enriched, and micronutrient-fortified diabetes-specific protein complement (DSPS) from Nutricia Worldwide Pvt Ltd–Danone India. The proteins have been sourced from each milk and soy.
The complement was added to Amul toned milk and was taken along with 30 grams of immediate upma or poha—two in style Indian savory breakfasts.
On the primary day of the examine, the contributors’ post-meal blood glucose and insulin ranges have been measured by the researchers at baseline, 30, 60, 90, 120, 150 and 180 minutes after breakfast to evaluate the consequences of the check product on post-meal blood glucose ranges.
The researchers additionally calculated the entire blood glucose and insulin ranges, the best blood glucose and insulin ranges, and the utmost improve in blood glucose and insulin ranges all through the three hours after breakfast.
For the following days, the contributors measured their glycemic variability (GV) utilizing steady glucose monitoring (CGM) at house.
Findings indicated that the entire blood glucose ranges within the check group three hours post-breakfast have been 59% decrease than the management group.
The height blood glucose ranges—or the best blood glucose studying—within the check group (192.7 ± 45.2 mg/dL) have been additionally considerably decrease than the management group (248.3 ± 52.3 mg/dL) three hours post-breakfast
One other metric, the utmost postprandial improve in glucose (ΔCmax), was additionally considerably decrease within the check group as in comparison with the management group by 46% (64.8 ± 27.3 vs 121.0 ± 39.9 mg/dL; p < 0.001).
No important variations between the 2 teams have been noticed when it got here to insulin ranges.
Glycemic variability
A considerably decrease glycemic variability was additionally seen within the check group in comparison with the management group, based mostly on CGM readings.
Glycemic variability (GV) was measured utilizing imply amplitude of glycemic excursions (MAGE) over the five-day check interval.
Outcomes confirmed that there was a considerably decrease GV throughout the check interval in comparison with the management interval, with MAGE of the check interval at 78.4 ± 23.1 mg/dL and that of the management interval at 93.0 ± 23.7 mg/dL.
A breakdown of the figures additional confirmed {that a} considerably decrease GV was seen within the check group solely throughout the daytime, with no important distinction noticed at evening.
Protein’s function in blood glucose regulation
The check group additionally noticed a considerably larger protein consumption in comparison with the management group.
Particularly, the imply protein consumption within the check group was 8.8 grams larger, with the check group’s imply protein consumption at 55.0 ± 11.9 g/day and 46.2 ± 11.7 g/day for the management group.
Vitality, carbohydrate, and fats intakes didn’t differ considerably between the 2 intervals.
Primarily based on present findings, protein may play a task in blood glucose regulation in diabetics by bettering insulin sensitivity and stimulating insulin secretion by way of amino acids from protein digestion.
Nonetheless, on this examine, there was solely a major improve in post-meal insulin on the thirtieth minute, which meant that the decrease post-meal glucose response was not because of larger insulin secretion.
On the a hundred and eightieth minute, there have been considerably decrease post-meal insulin ranges, which contributed to the general impartial impact on complete insulin ranges three hours post-meal. In response, the researchers defined that the decrease post-meal insulin ranges have been as a result of the low GI, excessive protein complement had lowered the glycemic load and thus decreased the physique’s insulin demand.
The researchers concluded that taking a low-GI, high-protein complement as a part of breakfast considerably improves postprandial glucose response with out considerably impacting insulin response.
“This examine in folks with T2DM confirmed that partial substitute of predominantly cereal breakfasts with DSPS considerably improved PPGR with out considerably impacting insulin response,” they wrote. “DSPS use additionally enhanced each day protein consumption and lowered GV all through the day in a real-world house setting.”
Supply: Diabetes Remedy. doi: 10.1007/s13300-025-01834-4. “Impact of a Diabetes-Particular Protein Complement (DSPS) on Postprandial Glycemic Responses in Adults with Sort 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Crossover Research in India”. Authors: Salis, S.S. et al.