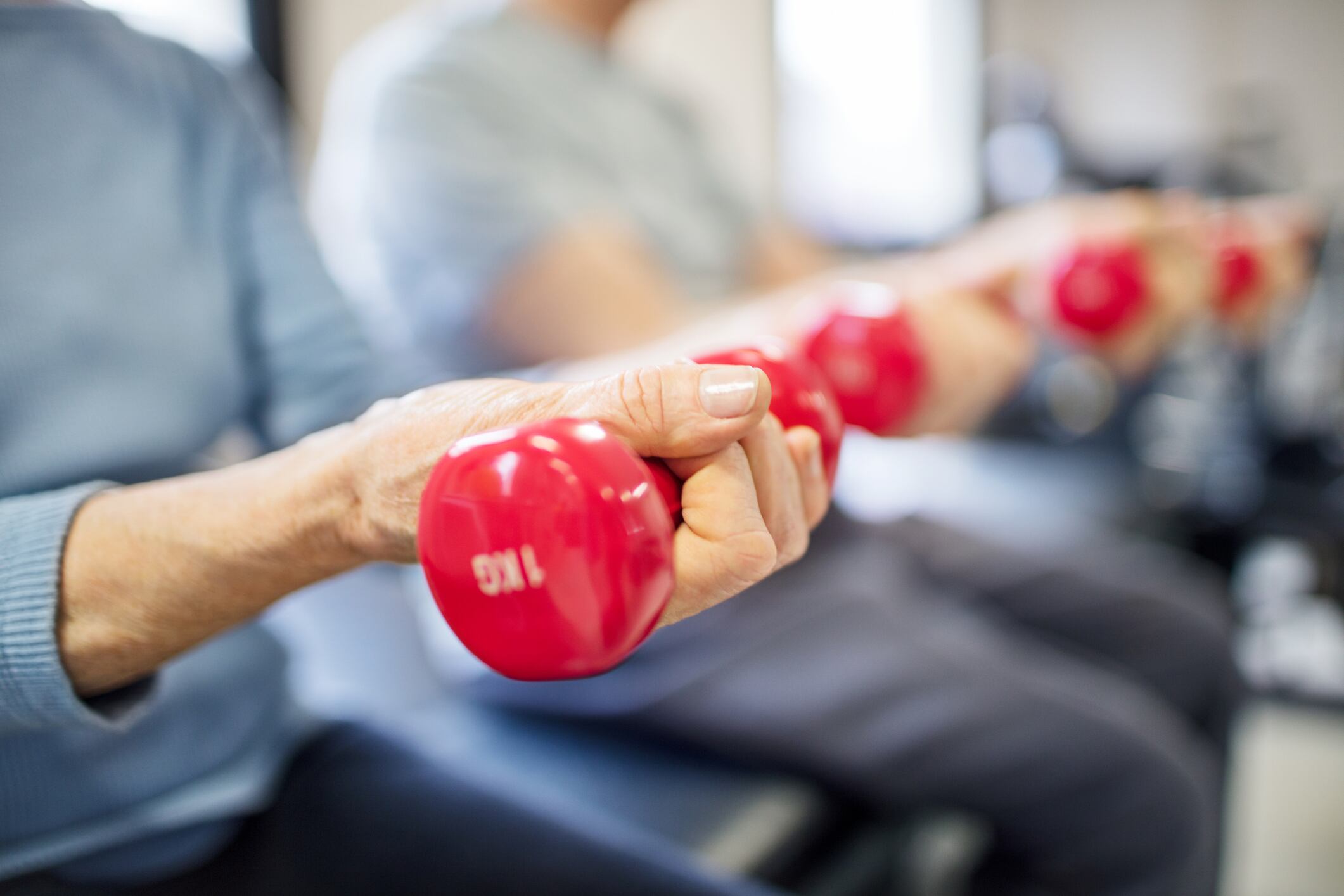
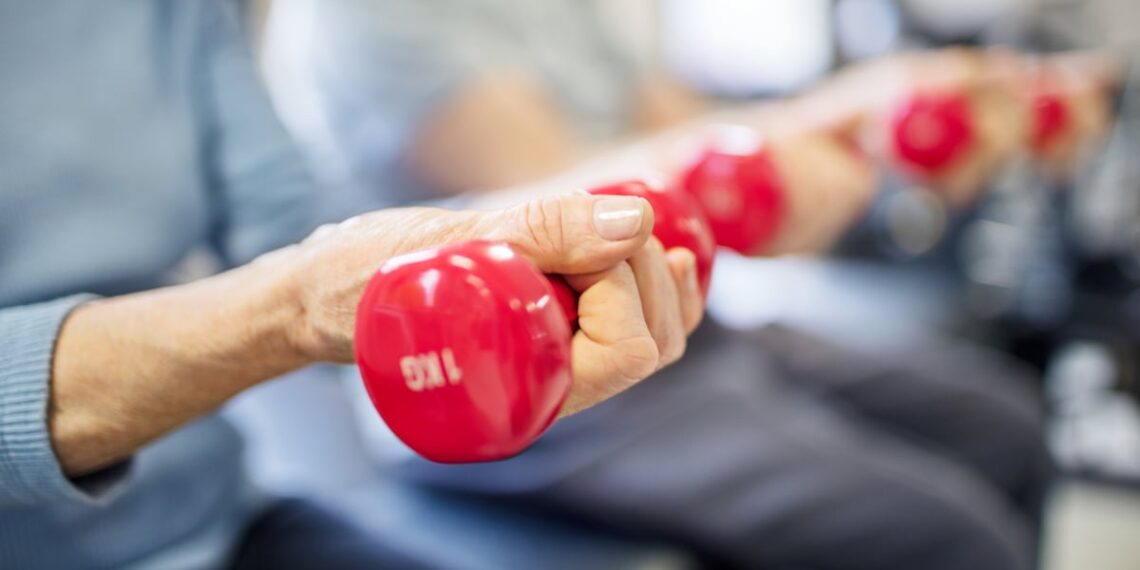
The randomized scientific trial, performed by researchers from the College of Texas Well being Science Middle, San Antonio, and printed in Dietetics, targeted on an understudied inhabitants: community-dwelling older adults with self-reported fatigue and lowered bodily perform.
Collected information indicated that, in comparison with placebo, the supplemented individuals confirmed higher enhancements in energy, mobility and endurance, together with reductions in fatigue and depressive signs.
One of the vital notable findings was the advance in chair stands within the supplemented group, which was almost 3 times higher than that noticed within the placebo group, suggesting enhanced muscular endurance and energy in individuals receiving BCAAs.
“These purposeful good points are clinically significant, as lowered gait velocity and poor 400 m stroll efficiency are established predictors of falls, hospitalization, lack of independence and mortality in older adults,” the researchers famous.
Though the outcomes are preliminary, with bigger research required to validate the findings, the examine presents priceless perception right into a prevalent and debilitating situation in older adults, with charges of fatigue starting from 25% in primary care to as high as 98% in long-term care settings.
“Few research have particularly focused community-dwelling older adults with reasonable fatigue or targeted on psychological fatigue outcomes, regardless of their relevance to high quality of life and purposeful independence,” the researchers wrote.
“The inclusion of individuals with elevated BMI and suboptimal purposeful standing additional enhances the scientific relevance, as these traits are prevalent amongst older adults in danger for bodily decline.”
BCAAS in older adults
Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs)—leucine, isoleucine, and valine—are important amino acids that play a key function in muscle protein synthesis.
A standardized 2:1:1 leucine:isoleucine:valine ratio (as used within the present examine) is often utilized in analysis and business merchandise.
BCAAs are quickly absorbed and could also be higher tolerated by older adults in comparison with entire protein or multi-nutrient dietary supplements, permitting for focused supply of anabolic amino acids comparable to leucine.
A number of research have explored BCAA supplementation for its potential to boost train efficiency, scale back muscle soreness and speed up post-exercise restoration.
Nonetheless, systematic critiques and meta-analyses have highlighted blended findings, attributing inconsistencies to variations in examine design, participant traits, dosing regimens and management for dietary protein consumption.
The present examine famous little is understood concerning the mixed results of BCAA supplementation and train in older adults experiencing fatigue.
“This hole is very essential given the heightened vulnerability of older adults to each bodily and psychological fatigue, and their underrepresentation in scientific trials,” the researchers wrote.
Research particulars
The target of this pilot, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial was to look at the affect of BCAA supplementation mixed with train on bodily and psychological fatigue, bodily efficiency and self-reported high quality of life in fatigued older adults.
Each acute (single-dose) and longer-term (8-week) results have been assessed to offer preliminary proof on feasibility, security and potential efficacy.
Twenty individuals (63% feminine; BMI: 35 ± 2 kg/m2; age: 70.5 ± 1.2 years) have been randomized to eight weeks of both train plus supplementation with BCAAs (100 mg/kg physique weight/d) or train plus a placebo.
This system included reasonable cardio and resistance coaching 3 times weekly. Bodily perform was assessed utilizing handgrip energy, chair stands, gait velocity, VO2 max and a 400 m stroll.
Psychological well being was evaluated utilizing the CES-D, Fatigue Evaluation Scale (FAS), Insomnia Severity Index (ISI) and international ache, fatigue and high quality of life utilizing a visible analog scale (VAS).
In comparison with placebo, the supplemented individuals confirmed higher enhancements in energy, mobility and endurance, together with reductions in fatigue (−45% vs. +92%) and depressive signs (−29% vs. +5%).
Time results have been additionally noticed for ISI (−30%), FAS (−21%), and VAS high quality of life (16%) following train + BCAA supplementation.
These preliminary outcomes recommend that BCAAs mixed with train could also be an efficient approach to enhance bodily efficiency and scale back fatigue and depressive signs in older adults. Limitations included the small pattern measurement and the pilot nature of the examine which restricted the generalizability of the outcomes.
The authors famous the potential for false positives will increase with a number of comparisons, particularly in a examine of this scale.
Additional, an imbalance within the intercourse distribution between the 2 teams could also be a limitation, as variations in female and male physiology may affect the metabolic response to supplementation and confound the outcomes.
The researchers famous that future research ought to incorporate complete dietary assessments to raised management for and consider the potential affect of background weight loss plan on intervention outcomes.
Supply: Dietetics. “Branched-Chain Amino Acids Mixed with Train Improves Bodily Perform and High quality of Life in Older Adults: Outcomes from a Pilot Randomized Managed Trial”. doi: 10.3390/dietetics4030032 (registering dot). Authors: Ronna Robbins, et al.