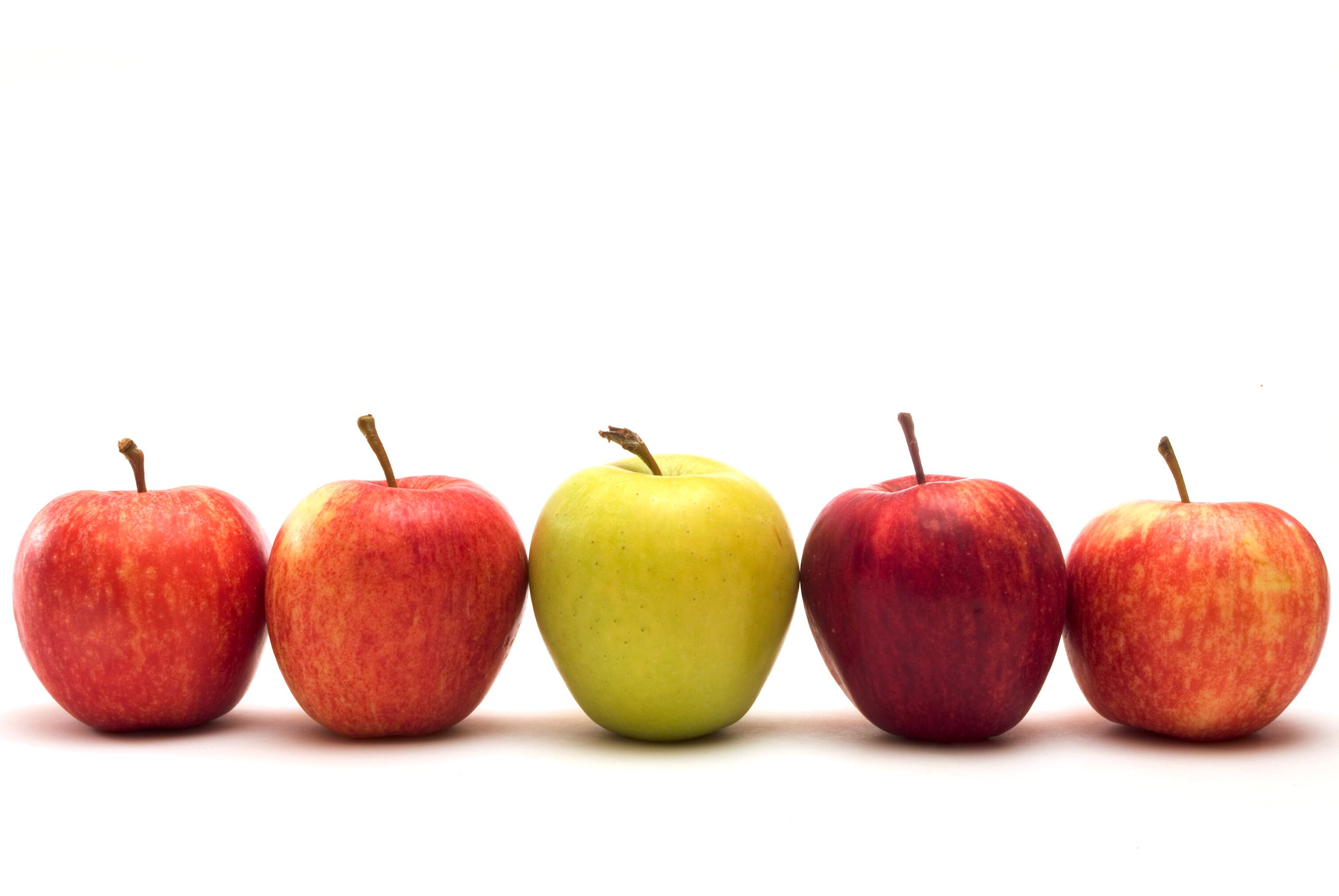
The in vitro research discovered distinct variations within the beginning microbial communities in lean and overweight samples. Apple fibers, significantly pectin, boosted useful species comparable to Akkermansia within the overweight microbial neighborhood and elevated useful metabolites.
The findings add additional proof to the function of food plan and the microbiome in tackling weight problems, highlighting the advantages of a personalised strategy.
“This in vitro research means that incorporating apple fibers into the diets of overweight people may help modify the composition of intestine micro organism and enhance metabolic well being,” researchers within the Netherlands and Spain wrote. “This personalised strategy may assist mitigate the consequences of weight problems.”
Influencing the microbial panorama
Rising proof suggests a pivotal function of food plan in influencing the intestine microbiota and danger of metabolic ailments.
Weight problems is https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1155/2018/4095789, and probiotics have emerged as potential anti-obesity agents.
Though the precise mechanisms have but to be confirmed, studies counsel that intestine microbes affect weight and adiposity by affecting gene expression, inflammatory pathways and the gut-brain axis. Sure micro organism are thought to guard towards visceral fats, and the absence of those species is related to weight problems.
Food regimen can modulate the microbiome and alter the range of micro organism. Dietary fibers in plant-based meals act as prebiotics for intestine micro organism, sustaining range and producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs).
SCFAs have many health benefits, together with anti-inflammatory, gut-protective, anti-obesity and immunoregulatory properties.
Nevertheless, though dietary fiber is understood to profit the intestine, its results could range from individual to individual, highlighting a have to tailor dietary interventions to an individual’s intestine microbiota.
“In different phrases, personalizing the food plan based mostly on particular person wants and well being circumstances is crucial for maximizing its effectiveness,” the present research famous.
Research particulars
The in vitro research collected stool samples from wholesome, lean and overweight people and used a bioreactor to simulate the digestion of apple, apple pectin and cellulose and their subsequent colonic fermentation.
The researchers used multi-omics evaluation to establish the important thing microorganisms and metabolites concerned.
Preliminary information urged that overweight and lean microbial communities had distinct beginning microbial communities. The apple fibers, significantly pectin, decreased Acidaminococcus intestini and boosted Megasphaera and Akkermansia within the overweight microbial neighborhood. The fibers additionally elevated the manufacturing of useful indole microbial metabolites.
“We discovered that the overweight microbial neighborhood had increased branched-chain amino acid catabolism and hexanoic acid manufacturing, probably impacting vitality steadiness,” the researchers wrote.
They discovered that apple pectin affected species like Klebsiella pneumoniae and constantly modulated the abundance of Bifidobacterium longum.
They famous that earlier animal research have proven a detrimental correlation between this species and weight problems, decreasing physique weight, lowering fats deposition and enhancing glucose tolerance.
As well as, they famous a “mutualistic cross-feeding relationship between Megasphaera sp. MJR8396C and Bifidobacterium adolescentis”.
The researchers indicated that the completely different results on the microbial communities noticed within the lean and overweight samples counsel that dietary fiber’s impression is determined by the intestine’s preliminary microbial composition.
They referred to as for additional research to substantiate their outcomes and discover the potential for personalised dietary interventions to enhance metabolic well being.