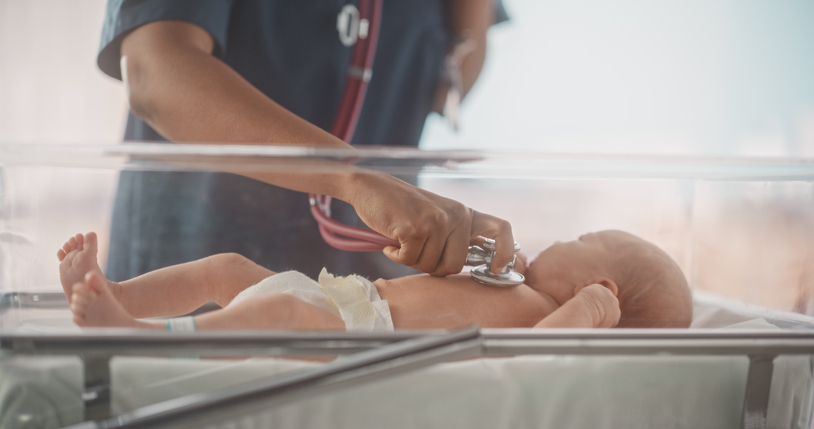
The research printed in Vitamins evaluated whether or not probiotics administered at clinician discretion profit preterm infants and assessed if the timing of probiotic initiation impacts their efficacy.
Probiotic supplementation for preterm infants has been a contentious situation as a consequence of a wide range of elements associated to the distinctive well being dangers of untimely infants, inconsistent analysis findings, regulatory issues, and the complexity of neonatal care.
Preterm infants and probiotics
Preterm delivery, outlined as a gestational age of lower than 37 weeks, ranks among the many main causes of loss of life in kids below the age of 5.
It is usually associated with various complications, reminiscent of respiratory misery syndrome (RDS), intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH), bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) and periventricular leukomalacia (PVL).
Studies utilizing next-generation sequencing have linked preterm birth-related morbidities, particularly NEC and sepsis, to the intestine microbiota. Dysbiosis, characterised by an absence of useful micro organism and an overgrowth of pathogens, performs a central function in each circumstances, as microbial imbalance mixed with the immature immune system and intestine barrier can result in extreme irritation, tissue injury and bacterial translocation.
Preterm infants are significantly inclined to microbial imbalances as a consequence of untimely delivery, extended antibiotic use, mechanical air flow and environmental elements.
Early microbiome assessments in preterm infants reveal colonization by pathogenic and hospital-associated micro organism, reminiscent of Staphylococci, Enterococcus spp. and Klebsiella spp.
In distinction, full-term infants primarily have microbiomes of vaginal, maternal fecal, or pores and skin origin, dominated by Lactobacilli spp. and Bifidobacterium spp. To counter these imbalances, neonatal care has lengthy used probiotic supplementation to forestall circumstances like NEC and sepsis.
Research particulars
The research concerned 330 extraordinarily low delivery weight (ELBW) infants. Of those, 206 consumed probiotics (60 early and 146 late) and 124 didn’t.
Findings indicated that probiotic supplementation, particularly combos of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, considerably decreased total mortality and mortality associated to NEC or LOS.
Early intervention with probiotics lowered total mortality, NEC/LOS-related mortality, and unrelated mortality, whereas late probiotic adminsitration decreased total and NEC/LOS-related mortality. Early probiotic use additionally accelerated the achievement of full enteral feeding.
The researchers concluded that probiotics decrease mortality and enhance feeding tolerance in preterm infants, highlighting the necessity for pointers on their use.
“We discovered that even within the absence of pointers and with choices to manage probiotics primarily on the discretion of clinicians, probiotics proceed to offer advantages to preterm infants,” they wrote.
They did nevertheless be aware that they didn’t get hold of knowledge on the intestinal microbiome, which restricted understanding of the way it interacts with probiotics, and advocate that future research on intestine microbiota in preterm infants completely examine the results of probiotics, significantly their relationships with acute well being issues and long-term end result.
As well as, the research known as for clearer pointers, noting: “It’s crucial for our neonatologists to ascertain standardized pointers to optimize probiotic effectiveness and improve outcomes for preterm infants.”
Pressure particular analysis wanted
Consultants on the current Worldwide Scientific Affiliation for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) assembly mentioned the relative risks of giving probiotics to preterm infants and emphasised the necessity for extra analysis.
Marketing consultant neonatal pediatrician Janet Berrington defined that whereas some research present probiotics cut back NEC and associated deaths, issues about potential dangers, reminiscent of sepsis, stay. Following an FDA warning in 2023, U.S. neonatal models decreased probiotic use, although UK models remained largely unaffected.
Berrington famous that elements like feeding practices and particular care models can affect probiotic effectiveness, suggesting extra knowledge is required to optimize their use.
Throughout a panel dialogue, consultants acknowledged the complexity of balancing the dangers of NEC and probiotic-related sepsis and highlighted the necessity for personalised care primarily based on particular person well being elements.
In addition they mentioned the shortage of consensus on probiotic strains and inconsistent NEC diagnoses, which complicates the dedication of probiotic advantages. The panel really useful future analysis give attention to evaluating totally different probiotic merchandise and dosages.
European pointers, reminiscent of these from ESPGHAN, conditionally advocate particular probiotic strains, whereas the UK’s Nationwide Well being Service (NHS) advises utilizing probiotics for preterm and at-risk infants however doesn’t endorse any single product.
Supply: Vitamins 2024, 16(17), 2995
doi: 10.3390/nu16172995
“Impression of Medical Use of Probiotics on Preterm-Associated Outcomes in Infants with Extraordinarily Low Delivery Weight.”
Authors: Wu, Wei-Hung et al.