Writing within the journal Frontiers in Vitamin, a group of Italy-based researchers performed a search of the Google Scholar and PubMed databases from inception to June 30, 2024 to investigate the revealed literature on these various protein sources and their potential roles in scientific diet.
“The quests of those proteins and derived peptides within the context of preventive and scientific diet current a promising highway to uncover modern dietary methods and therapeutic approaches,” they wrote, noting that the search additionally responds to environmental issues.
With the global food demand is expected to increase from 21% to 56% between 2010 and 2050, not solely does the rising consumption of purple and processed meat contribute to the well being burden however considerably impacts the atmosphere because of increased greenhouse fuel emissions, consumption of water and land use and human-induced terrestrial biodiversity loss.
Breaking down the proteins
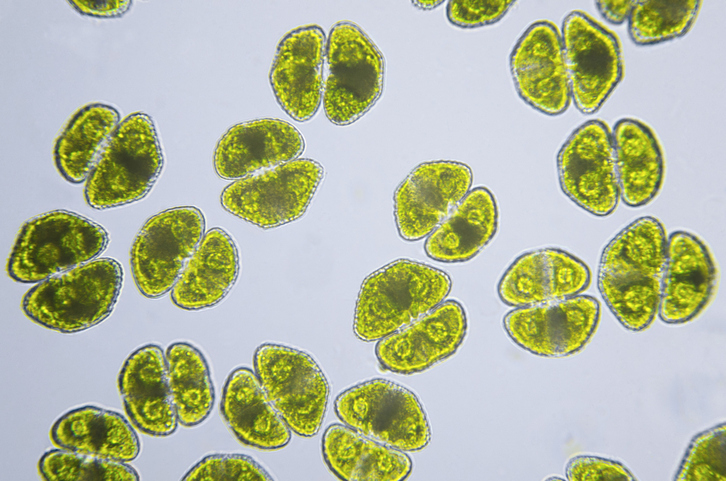
The researchers famous that algae are protein-rich marine assets which have a fast development price, can adapt to excessive and aggressive environments and include quite a few health-promoting compounds and proteins, resembling lectins, phycobiliproteins, mycosporine-like amino acids, derived hydrolysates and bioactive peptides.
“Commercially out there microalgae, resembling spirulina (Cyanobacterium Arthrospira platensis) and Chlorella vulgaris include as much as 68% protein by dry weight, whereas purple algae include as much as 47% of protein,” they wrote.
In accordance with their evaluation, the proof means that algae-derived proteins might assist to counteract muscle loss within the ever-expanding older inhabitants and may be harnessed for his or her anti-inflammatory, anti-microbial, anti-tumor, anti-diabetic, anti-hypertensive, antioxidant properties and anti-obesity results.
Consumption of protein from fungi—mycoprotein—as various with a low environmental footprint is rising globally.
The evaluation highlighted potential advantages together with weight administration by decreasing vitality consumption and will increase satiety; cardiometabolic well being by advantageously modifying blood lipid profiles; and rising muscle protein synthesis, significantly in younger people.
Concerning insect protein, the researchers reported that whereas it’s difficult to generalize the dietary profile of the two,100 bugs species thought-about edible, many are sources of high-quality protein, unsaturated fat, micronutrients and fiber.
“Apparently, iron and zinc present in crickets, grasshoppers and mealworms have been proven extremely bioavailable in comparison with sirloin beef,” they wrote. “At the moment, widespread edible insect species are home cricket (Acheta domesticus), African palm weevil (Rhynchophorus phoenicis), yellow mealworm (Tenebrio molitor), mopane worm (Gonimbrasia belina), domesticated silkworm (Bombyx mori) and honeybee (Apis mellifera).”
The evaluation highlighted the potential of insect protein to help muscle proteins synthesis for muscle constructing in populations that devour much less protein and endure from anabolic resistance such as older and the clinically compromised. Though human research are nonetheless missing, peptides and bioactive compounds derived from edible bugs might additionally present antioxidant, anti-obesity, anti-diabetic and anti-hypertensive advantages.
The challenges
Regardless of the potential well being advantages, there are challenges to beat, resembling security issues and cultural acceptance of other sources of protein within the eating regimen.
“Meals disgust (the product goes past the internalized norm of what meals is), lack of familiarity with insect consumption, neophobia (hesitance to devour unfamiliar meals), lack of product data, curiosity or sensation searching for and meals know-how neophobia had been the recognized drivers for low acceptance of insect consumption,” the researchers wrote.
The evaluation referred to as for future research to analyze the protection, efficacy and sensible utility of those various proteins in scientific diet and famous the necessity for social and behavioral change methods to alter individuals’s attitudes in the direction of these novel meals.
Supply: Frontiers in Vitamin Quantity 11 – 2024
doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1461621
“The function of algae, fungi, and insect-derived proteins and bioactive peptides in preventive and scientific diet”
Authors: M. A. Yimam et al.