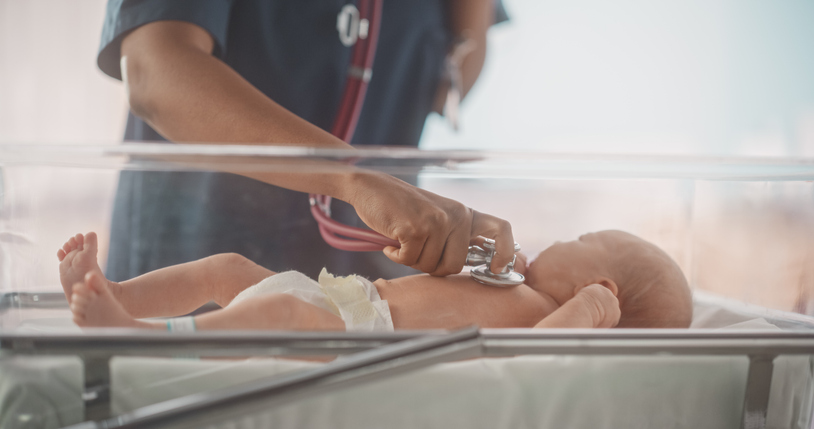
As advisor neonatal pediatrician Janet Berrington defined throughout a panel dialogue on the occasion in Cork, Eire, probiotics have lengthy been thought of a helpful addition to the healthcare of preterm infants, particularly in stopping life-threatening circumstances like necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC).
The panel—which included pediatric medical professionals and representatives from Biotic Options Consulting and the NEC UK Charity—famous the numerous variations in sensible software and acceptance of probiotics throughout the globe.
NEC and probiotics
NEC, the damage or irritation of intestinal tissue, is reportedly the commonest severe gastrointestinal illness in preterm infants and a distinguished single reason behind dying in extraordinarily preterm infants between two weeks and two months of age.
Some research have discovered that probiotics can significantly reduce the incidence of NEC, general mortality and NEC-related mortality in untimely infants, nevertheless debate continues concerning the affect of the probiotics.
In September 2023, the FDA released a warning towards the danger of “invasive, probably deadly” sepsis with probiotics and the unregulated nature of the market following the dying of a preterm toddler administered a probiotic as a part of in-hospital care.
Previous to FDA warnings, as much as 29.1% of neonatal intensive care models (NICUs) administered probiotics to premature neonates in line with latest analysis, nevertheless, this decreased significantly after the FDA warning was issued.
In accordance with Berrington, the U.S. ruling appeared to haven’t any affect on the perspective of NICUs within the UK, with roughly two-thirds of neonatal models incorporating them into their care protocols.
Throughout Europe, utilization is simply as assorted. One research assessing the use of probiotics in preterm infants in European NICUs discovered that in 2021, 21% of French NICUs however 100% of Swiss NICUs reported routine probiotic use.
In questionnaire responses, the principle obstacles to routine probiotic use had been the absence of suggestions, lack of consensus on pressure choice, inadequate scientific proof and considerations relating to potential hostile results.
Probiotic effectiveness
Research have proven that the effectiveness of probiotics can fluctuate based mostly on the setting, and components corresponding to feeding practices and antibiotic use can affect outcomes.
Berrington referenced a latest UK research involving stool samples from 13 neonatal ICUs, which discovered the particular care unit was probably the most vital issue affecting intestine microbiota, outweighing different variables like mode of supply and feeding practices.
She famous extra understanding of unit-specific practices is required to optimize probiotic effectiveness.
The panel agreed all medical choices include inherent dangers, and right here the danger of probiotic-related sepsis should be weighed towards the danger of NEC.
Nonetheless relative dangers and advantages fluctuate based mostly on particular person beliefs {and professional} opinions, resulting in potential frustration amongst dad and mom and clinicians.
Personalised Care
Talking to NutraIngredients following the panel dialogue, Berrington famous that the complexity of circumstances like NEC requires a nuanced method.
“It is unrealistic to count on a one-size-fits-all resolution because of the myriad of things influencing a child’s well being,” she stated. “Superior knowledge evaluation, together with AI, may assist unravel these complexities by integrating microbiome, metabolomic and genomic knowledge.”
Furthermore, inconsistent analysis of NEC amongst clinicians provides one other layer of complexity, making it troublesome to evaluate the true affect of probiotics, she defined, whereas “the dearth of standardized reporting on probiotic administration complicates this course of”.
She added that conducting placebo-controlled trials for probiotics in neonatal care presents moral challenges, so a possible subsequent step in analysis could possibly be to check completely different probiotic merchandise, dosages and administration schedules – areas at present missing ample knowledge.
“It is going to be fascinating to see if NEC charges will rise within the U.S. attributable to restricted entry to probiotics, however solely time and complete knowledge evaluation will verify this,” she stated.
European pointers
The European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Vitamin (ESPGHAN) launched pointers in September 2022 on probiotic supplementation in preterm infants.
“There’s at present inadequate high-quality proof to suggest one probiotic product over the opposite,” the report reads.
“Models are subsequently beneficial to decide on one of many mixture pressure merchandise listed that has confirmed effectiveness and to develop an area SOP/formulary along with native microbiology and pharmacy groups based mostly on the proof and steering supplied inside this guideline.”
The three merchandise, manufactured in line with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs), are: Labinic (Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium bifidum and Bifidobacterium Infantis), ProPrems (Bifidobacterium Infantis, Bifidobacterium lactis and Streptococcus thermophilus) and Infloran (Bifidobacterium bifidum and Lactobacillus Acidophilus).
ESPGHAN advises that probiotics be given to all infants born earlier than 32 weeks gestation, all very low start weight preterm infants and all different infants liable to dysbiosis who could profit from probiotics (e.g., brief intestine/gastroschisis).