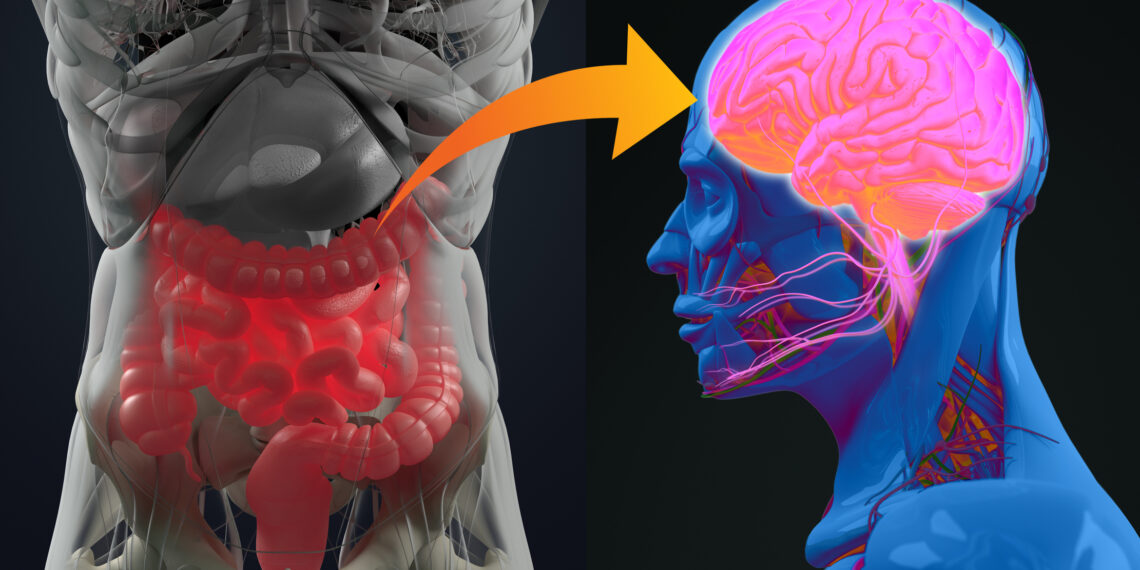
Scientists are more and more recognizing how interactions between the intestine and mind form the illness and creating therapeutic strategies that concentrate on α-synuclein, the hallmark ‘abhorrent protein’ of PD.
Analysis has proven that inhibiting α-synuclein is a key technique for illness modification. Of their evaluate, the authors explored how polyphenols affect intestine microbiota and the way this may occasionally doubtlessly improve the modulation of α-synuclein aggregation.
“Understanding the interplay between polyphenols and intestine microbiota and figuring out which particular microbes might improve the efficacy of polyphenols is essential for creating therapeutic methods and precision vitamin based mostly on the microbiome,” they wrote within the journal Vitamins.
New give attention to the intestine
An estimated 1.5 million folks in the US reside with PD, with 60,000 Americans diagnosed each year. PD is a progressive neurological dysfunction that primarily impacts motor perform, resulting in signs including tremors, stiffness and slowness.
Considered one of PD’s hallmark pathologies is accumulation of alpha-synuclein (α-synuclein). It is a presynaptic neuronal protein that aggregates into insoluble fibrils, forming Lewy our bodies (LBs) and Lewy neurites in the brain. To date its precise perform just isn’t absolutely understood. Nevertheless, irregular accumulation contributes to neurone death and the symptoms of PD.
Earlier PD research tended to give attention to the mind, however now the gastrointestinal (GI) system is acknowledged as pivotal in PD pathogenesis. Latest analysis has more and more targeted on the intestine–mind axis: a posh bidirectional communication system connecting the entire enteric nervous system (ENS) of the GI tract with the central nervous system (CNS).
Rising proof means that α-synuclein pathology might begin within the intestine after which unfold to the mind by the vagus nerve. This concept has been supported by observations of GI abnormalities in PD sufferers years earlier than the beginning of motor signs. Plus, alterations in intestine microbiota composition have been noticed in PD sufferers, exhibiting the potential function of intestine dysbiosis within the illness’s development.
Polyphenols are recognized for his or her antioxidant and anti inflammatory properties. In addition they affect the composition and performance of intestine microbiota. By modulating the intestine microbial group, dietary polyphenols might scale back intestinal irritation, improve intestine barrier perform and produce metabolites that would doubtlessly inhibit the aggregation of α-synuclein.
This implies understanding the mechanisms behind interactions between dietary polyphenols, the intestine–mind axis and α-synuclein pathology might open new avenues for stopping or slowing the development of PD.
Exploring ‘a brand new frontier’
The researchers described the intestine–mind axis as a “new frontier in PD”. They discovered proof that PD pathogenesis could also be influenced by the interaction between the imbalance of gut microbes and altered bacterial metabolites. Findings in each PD affected person research and experimental animal research have revealed intestine micro organism assist regulate anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory profiles. This implies that alterations within the intestine microbiome can influence the risk of developing PD.
The authors discovered some PD sufferers have proven elevated lipopolysaccharide serum ranges—which might correlate to increased intestinal permeability. As well as, the heart of PD sufferers are sometimes colonized by lipopolysaccharide-producing micro organism which causes continual irritation and degradation of gut mucosal lining.
Biopsies of GI tissues from PD sufferers have proven α-synuclein accumulation within the decrease components of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, colon and rectum. Discovering α-synuclein exterior the CNS helps the speculation that the presence of α-synuclein in each the mind and the intestine might outcome from a standard pathological aggregation pathway involving the vagus nerve.
EGCG, quercetin, polyphenolic acids, curcumin and their derivatives are a few of the most well-known and efficient polyphenolic inhibitors of α-synuclein.
Polyphenols as promising brokers
The authors concluded that dietary polyphenols make promising brokers for PD prevention due to their abundance and relatively low toxicity.
Polyphenols confirmed advantages in animal fashions of PD—with proof from epidemiological research demonstrating the affiliation between polyphenols and a diminished threat of creating PD. Nevertheless, knowledge from randomized managed trials in sufferers with pre-existing PD are at the moment restricted. The researchers mentioned this implies future scientific research are essential to guage the effectiveness of dietary polyphenols in slowing PD development.
“Extra targeted analysis is required to completely perceive the mechanisms between polyphenols, the intestine microbiota and α-synuclein with a purpose to set up the therapeutic viability of polyphenols in scientific settings,” they wrote.
Supply: Vitamins 2024, 16(13), 2041
doi: 10.3390/nu16132041
“Intestine–Mind Axis in Focus: Polyphenols, Microbiota, and Their Affect on α-Synuclein in Parkinson’s Illness.”
Authors: Elizabeth Riegelman and Jia-Sheng Wang