In response to the outcomes, the totally different components of the fruit include ranges of vitamins corresponding to phenolic compounds and antioxidants rivalling these of established superfruits, wrote Beatriz C. B. S. Mello, researcher on the Federal College of São Carlos, Buri, Brazil, and colleagues in Antioxidants.
Commenting independently, Inna Yegorova, founder and proprietor of the nutraceuticals consulting agency Inna Consulting informed NutraIngredients that the research “supplies a sturdy basis for increasing analysis into this promising fruit.”
“Understanding the antioxidant capability helps place Jerivá as a superfood, which might appeal to curiosity from health-conscious shoppers and the wellness business,” she mentioned.
A nutritious fruit
Most fruits are wealthy sources of important vitamins together with nutritional vitamins, minerals and phenolic compounds, which can be utilized as pure components to meals merchandise, sid the researchers. “The data and use of untamed fruits in human vitamin could possibly be a great supply for public insurance policies towards malnutrition,” they added.
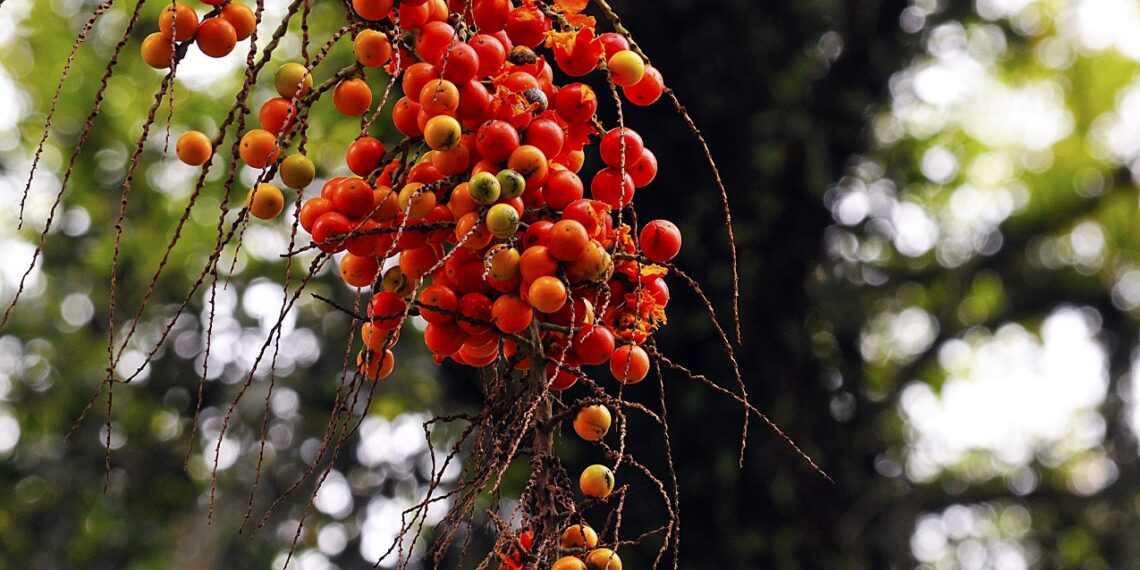
Jerivá (Syagrus romanzoffiana) grows abundantly on palm timber in tropical and subtropical components of Latin America. Nearly half of the fruit (47%) consists of the pulp, with the seed and the peel making up 43% and 10% of the fruit respectively. As an alternative of human consumption, the fruit is principally used as animal feed or thrown away, and no research have analyzed the dietary advantages of every a part of the fruit, be aware the investigators.
Profiling the peel, pulp and seeds
Within the newest research, the analysis workforce collected Jerivá fruits in Brazil then washed, sanitized and peeled them. As soon as the peel, pulp and seeds have been separated, the workforce dried them and floor them in a knife mill earlier than freezing them and measuring their nutrient ranges.
In response to outcomes from spectrophotometry, the researchers discovered that each 100g of dry matter (dm) of Jerivá seeds contained 12.0mg of vitamin C, much like the fruit of persimmon. The peel and pulp in the meantime have been extra akin to blackberries with 81.7mg and 92.3mg per 100g dm respectively. They added that the fruit “might be thought of a great various for vitamin C consumption” and may help individuals to hit their really helpful dietary allowances of the vitamin.
From colorimetry research, Mello and colleagues noticed that the pulp and peel are wealthy sources of phenolic compounds, much like high-phenolic-level fruits such because the banana passionfruit, with 1089 and 971 gallic acid equivalents (GAEs) per 100g dm respectively. Particular polyphenols detected by excessive efficiency liquid chromatography (HPLC) included hydroxy benzoic acid, procyanidin B2, coumaric acid and ferulic acid.
The workforce used assessments corresponding to Trolox Equal Antioxidant Capability (TEAC) to evaluate the fruit’s antioxidant capability. They discovered that the pulp had antioxidant ranges of three.5 mmol Trolox equivalents (TEs) per 100g dm, the extent of concentrated lingonberry – a well-known superfruit. In the meantime, the seeds had 1.7 mmol TEs per 100g dm, placing them on a stage much like pomegranates.
The researchers additionally discovered that the antioxidant capability strongly correlated with the overall phenolic content material, and vitamin C was chargeable for 6.2% of antioxidant capability within the peel in contrast with 4.7% and 1.4% within the pulp and seeds respectively. Because of this, the workforce concluded that “the phenolic compounds are chargeable for the antioxidant capability” on this fruit.
By way of carotenoids corresponding to (all-E)-β-carotene, (9Z)-β-carotene and (all-E)-lutein, the peel beat the pulp, with HPLC-derived ranges of (all-E)-β-carotene (5.16 mg per 100 g dm) akin to that of papaya fruit.
“The synergistic impact of all of the compounds discovered within the fruit could possibly be optimistic and stimulate fruit consumption and analysis,” say Mello and colleagues. They add that “[t]he data of all these properties might be an incentive to business use of the fruit, in addition to its use as an ingredient in a number of formulations within the meals.”
Commercializing Jerivá
Jerivá could possibly be utilized in many several types of meals merchandise, corresponding to a flour substitute or taste or dietary enhancement in bread, muffins and cookies, and an ingredient so as to add to the feel of vitality bars, granola, and snack mixes, Yegorova mentioned.
Nonetheless, its widespread use faces some challenges, together with restricted consciousness and analysis into its properties, she famous.
“Establishing a dependable provide chain for Jerivá entails addressing points associated to cultivation, harvesting, and processing. Guaranteeing sustainable and moral practices might be difficult,” she mentioned, including that establishing processing strategies and gaining regulatory approval are vital hurdles.
Supply: Antioxidants 2024, 13(6), 711
“Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Capability of Pulp, Peel and Seeds from Jeriva (Syagrus romanzoffiana)”
doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13060711
Authors: Beatriz C. B. S. Mello et al.