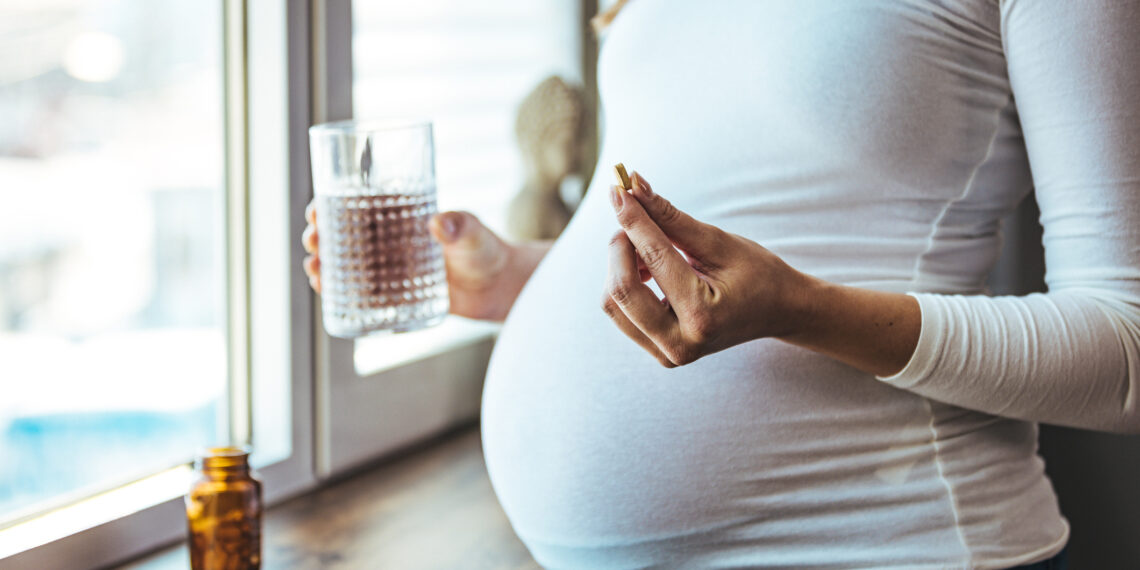
Most research into periconceptional folic acid (FA) dietary supplements deal with the results on fetal improvement. Nevertheless, the Chinese language researchers behind this tudy acknowledged a scarcity of population-based analysis on the affiliation between utilizing FA throughout being pregnant and the placenta’s improvement.
To handle this, they investigated the influence of FA supplementation in numerous pregnancies on placenta-related parameters at supply in ladies recruited from Ma’anshan Metropolis, Anhui Province in China between Might 2013 and September 2014.
Total, the researchers famous that, “FA use earlier than conception may enhance placental width and space, and FA use in early/center being pregnant may enhance placental thickness.”
They referred to as for additional research to verify the findings.
Inconsistent outcomes
The placenta is a brief endocrine organ that facilitates gasoline, nutrient and waste exchange between maternal and fetal compartments. FA deficiency results in disruption of DNA methylation and regular epigenetic regulation. This may have an effect on placental improvement and performance, result in changes in fetal programming and increase the risk of some diseases in adulthood.
A number of research have discovered that FA supplementation is useful for the discount of homocysteine ranges. Homocysteine can induce placental endothelial cell injury, have an effect on the expansion and development of the placenta and fetus and induce preeclampsia.
Present research on the results of FA supplementation on placental improvement have been inconsistent, nevertheless. One survey reported that pregnant ladies taking 5 mg of FA a day had an 11.9% common enhance in placental weight compared to those not taking it. In distinction, some research have discovered that FA supplementation is not associated with placental weight.
Placental weight is related to birth weight, due to this fact when folic acid straight impacts placental development and improvement, it additionally not directly impacts fetal development.
“Placental weight is simply one of many indicators of placental improvement and can’t totally clarify the event of the placenta,” the researchers wrote. “This research makes an attempt to comprehensively examine the results of FA supplementation in numerous pregnancies on placental improvement from a number of dimensions.”
Measuring the placenta
The research collected knowledge on FA use from one month earlier than conception to supply. Contributors had been recruited at their first antenatal care go to at Ma’anshan Maternal and Little one Well being Care Heart. In whole, 2,708 had been included within the last evaluation.
To evaluate use of FA dietary supplements in numerous intervals, all contributors had been requested to finish a questionnaire at their routine obstetric go to. It coated the date complement use started, frequency of use (occasions/week), dose and complement model.
Knowledge on placental dimension and form had been measured after beginning inside half an hour by skilled personnel. First, the placenta was expanded on a flat floor. Then the longest size of the placental floor was measured together with the maximal diameter utilizing a clear plastic ruler. Placental thickness was measured on the thickest level.
Primarily based on a number of regression evaluation, researchers used propensity rating weighting to reinforce comparability between totally different FA supplementation teams.
Elevated width, space and thickness
The researchers famous that when evaluating supplemented and non-supplemented teams, FA supplementation earlier than conception was related to elevated placental width and floor space. Additionally they discovered that FA use in early/center being pregnant was associated to elevated placental thickness.
“In conclusion, our research supplied proof that FA supplementation at totally different phases of being pregnant had a possible influence on placental improvement,” they wrote, speculating that the outcomes are because of the truth that periconception folic acid supplementation might trigger epigenetic modifications within the preimplantation embryo, which can then lead to elevated placental and fetal development patterns.
As limitation, the studynoted that the dearth of dietary data prevented them from evaluating the impact of dietary folate. The restricted knowledge from comparable research was additionally cited as constraint, and potential interactions amongst a number of nutritional vitamins weren’t taken under consideration.
Supply: Vitamins
doi: 10.3390/nu16111729
“Placenta-Associated Parameters at Supply in Relation to Folic Acid Supplementation in Totally different Pregnancies”
Authors: Yating Ren et al.