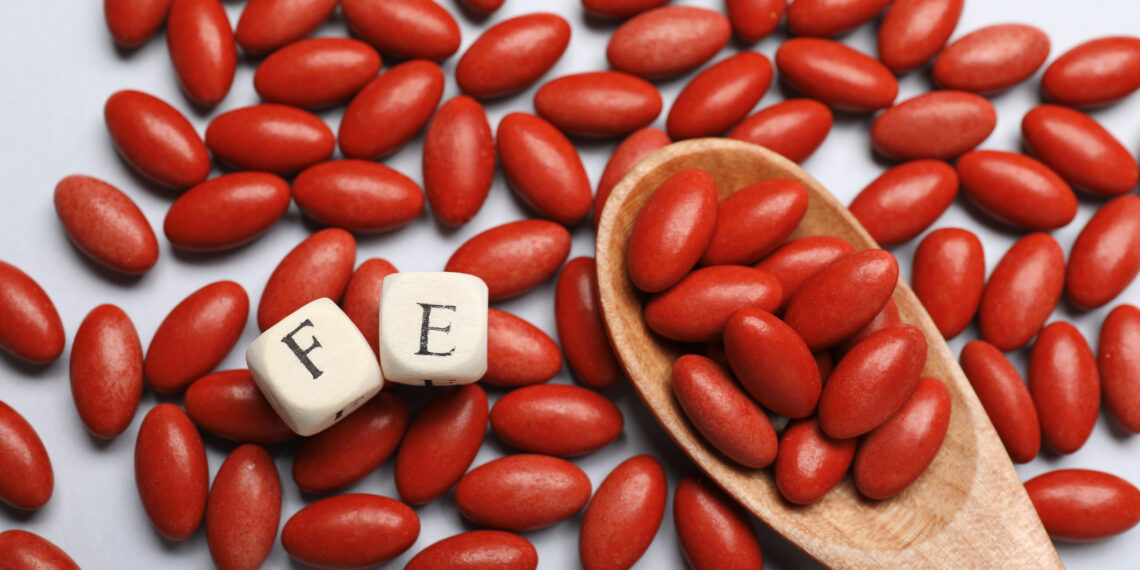
In a report revealed on June 12, EFSA’s Panel on Nutrition, Novel Foods and Food Allergens (NDA) concluded concluded that there’s not sufficient proof to ascertain a TUI for iron—a most consumption stage that may be consumed every day over a lifetime with out antagonistic well being results.
As an alternative, it has agreed on a ‘secure stage’, which is the utmost quantity it might confidently conclude poses no threat of antagonistic results within the basic inhabitants.
The extent relies on the information associated to the prevalence of black stools—a sign of great unabsorbed iron within the GI tract and could also be a primary signal of iron metabolism dysfunction previous to iron overload and toxicity.
Knowledge means that black stools don’t happen at supplemental iron intakes of 20 to 25 mg/day (added to a background consumption of 15 mg/day), due to this fact the panel established a secure stage of consumption for iron of 40 mg/day for adults (together with pregnant and lactating ladies).
Allometric scaling was then used to substantiate secure ranges for kids: 10 mg/day for these between the ages of 1 and three years; 35 mg/day for these between 15 and 17 years; and 5 mg/day for infants between 4 and 11 months, protecting iron intakes from fortified meals and meals dietary supplements however not from toddler or follow-on system.
These don’t apply to people who obtain iron beneath medical supervision as a therapy for iron deficiency anaemia.
The iron situation
Controlling anemia is a world well being precedence for the World Well being Group (WHO), which goals to chop anemia prevalence in ladies in half by 2025.
Iron deficiency anemia primarily impacts premenopausal and pregnant ladies, rising youngsters and the aged, nonetheless, it’s also more and more acknowledged as a complication of a number of illnesses related to way of life and dietary patterns, corresponding to weight problems, inflammatory bowel illness, colorectal most cancers or power kidney illness
There are numerous various kinds of oral iron dietary supplements accessible however essentially the most generally prescribed oral iron is ferrous sulphate. Ferrous iron dietary supplements are efficient; nonetheless, they’ve a excessive frequency of unwanted side effects compared to ferric iron sources. In reality, up to 60% of people taking oral iron dietary supplements report gastrointestinal unwanted side effects.
Widespread unwanted side effects embrace oxidative stress, abdomen pains, constipation, diarrhea, lack of urge for food, nausea and darkish stools.
That is as a result of poor bioavailability and excretory mechanism of iron dietary supplements within the physique, resulting in a build-up and oxidative reactions. Lengthy-term overdosing of the mineral has even been linked with colon cancer biomarkers.
Nélida Leiva Eriksson, affiliate professor at Lund College, Sweden and founding father of Ironic Biotech, a start-up that goals to convey a very bioavailable new supply of iron to market, mentioned this replace raises consciousness of the toxicity of iron dietary supplements.
“This has been ignored for a very long time, and that’s the reason it’s not unusual to seek out tablets of as much as 360 mg in the marketplace, and pregnant ladies obtain doses greater than 60 mg.”
Efforts to ascertain a secure restrict
In 2004, EFSA’s NDA Panel revealed a scientific opinion stating that the information accessible at the moment have been inadequate to ascertain an higher restrict for iron.
The European Fee due to this fact requested a evaluation of this scientific opinion primarily based on newly accessible proof.
The College of Copenhagen, in collaboration with the College of Oslo and the Karolinska Institutet, performed a scientific literature evaluation of human intervention and observational research for EFSA. Primarily based on this proof, the panel assessed the potential damaging influence on well being associated to excessive iron consumption.
It once more discovered inadequate information to find out an higher restrict for iron and as an alternative suggested on the utmost quantity that EFSA can confidently conclude poses no threat of antagonistic results within the basic inhabitants, known as the secure stage of consumption.
The panel additionally supplied suggestions for the analysis neighborhood, suggesting the necessity to examine: the impact of accelerating doses of (haem and non-haem) iron on GI tract physiology, pathology and on the microbiome, the mechanisms of interactions between excessive intakes of iron and the absorption and metabolism of different minerals (corresponding to copper, zinc, calcium and manganese), the physiological limits for iron homeostasis, and the extent of iron absorption for prime iron intakes over a chronic time period.